Magento is offered in two flavours, the cloud-deployed and hosted Commerce for enterprises, and the Open Source eCommerce for self-management with a large community backing.
The free open source edition, as covered in this post, is a flexible platform for developers and small businesses alike. It comes with the performance and features to meet the requirements of the businesses of today as well as the capacity to grow in the future.
If you are looking for the perfect platform for your growing small business or would wish to learn and experiment with building an online store, deploying Magento Open Source in the cloud is a great way to get started. However, while Magento can run well on any cloud, picking your provider by price or brand name might leave you betting on a slow horse.
In order to help newcomers and seasoned online retailers alike to make an educated decision, we benchmarked Magento on some of the most popular cloud providers.
Benefits of benchmarking
The ability to empirically test and verify system performance can be a valuable tool in server management. With repeatable and host agnostic benchmarking, anyone can produce comparable results for a number of use cases.
While often small in effect, some of the server settings might have an impact on the server performance and customer experience. Running benchmarks to validate your configuration can provide reassurances of consistency and reliability. The benchmark plan provided by Magento also tests a number of common customer action to ensure the web server is functioning correctly.
Balancing the server resources to match your customer demand can be a cost-effective way to save on cloud hosting. Knowing the real world performance numbers for your storefront can help in reducing the overhead. Scaling down system configuration while retaining snappy response times will keep both your customers and your bottom line happy.
Benchmarking a number of different configurations also allows you to optimize the system resources for the best bang for the buck. The web server might be perfectly happy with the amount of memory available but would benefit from additional CPU cores. Or that a large product database is getting bottlenecked by the lack of RAM and slow storage while the processor would comfortably reply to more requests.
Lastly but perhaps most importantly, the benchmarks of comparing cloud providers themselves. Even when the server configurations might look the same in theory, their capacity to serve customers could be entirely different. The only way to reliably determine these differences is to run the benchmarks on all candidates.
Server configurations
The main focus of our benchmarks was on the differences between the providers. To ensure comparable results, we ended up running two sets of benchmarks to minimize the variables. One to compare the performance of the system resources, and another to compare the price to performance. Dividing the benchmarks into these two tests helped to account for the varying configuration and pricing options, while also providing a better overview of the results.
In the resource-focused benchmarks, the cloud servers were configured with 4 GB of RAM and 2 CPU cores according to the similar instances available most providers. While during the second test each system was configured to the equivalent of $40 per month.
The Magento Open Source edition was set up identically on each provider according to our installation guide.
Each server was deployed to either London or Amsterdam data centres when available with the average latency to the load generator between 10-20ms.
Benchmarking methods
For an objective comparison, we used the recommended procedures as described by the instructions in the Magento Performance Toolkit. The methods and configurations are also outlined in our Magento benchmarking guide to increase transparency and repeatability.
The benchmark plan provided by the Performance Toolkit version 2.3-develop was run using the Apache JMeter load generating software on a desktop-grade computer.
As the aim of these benchmarks was to evaluate the system capabilities specifically, we also monitored latency during testing to minimize the effect of the network quality. While slow connectivity itself would not have been an issue, erratic changes in latency might reflect poorly on the response times.
Results
The benchmarks were performed multiple times on each Magento server. This was done to establish the average performance that could be expected from instance to instance. The results displayed are based on the average runs.
Resource normalized comparison
In these benchmarks, each cloud server was configured with the same allocated resources of 2 CPU cores and 4 GB of system memory. This configuration was chosen as an affordable starting point for new online stores while allowing room to grow.
| Normalized by server resources | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWS EC2 | DigitalOcean | Linode | UpCloud | |
| Configuration | 2 CPU / 4 GB / 30 GB | 2 CPU / 4 GB / 80 GB | 2 CPU / 4 GB / 48 GB | 2 CPU / 4 GB / 80 GB |
| Throughput | 1482.68 / minute | 904.625 / minute | 947.957 / minute | 2089.506 / minute |
| Average | 574 ms | 1200 ms | 1135 ms | 327 ms |
| Deviation | 1179 ms | 2322 ms | 2367 ms | 618 ms |
| Latency | 18.8 ms | 16.9 ms | 14.3 ms | 18.1 ms |
| Cost | $ 80.82 | $ 20 | $ 20 | $ 20 |
Although every server in the comparison was created with the same system configuration, some major differences in capabilities are immediately observable. As the available memory on the servers was the same, the benefit here comes down to the CPU and disk performance.
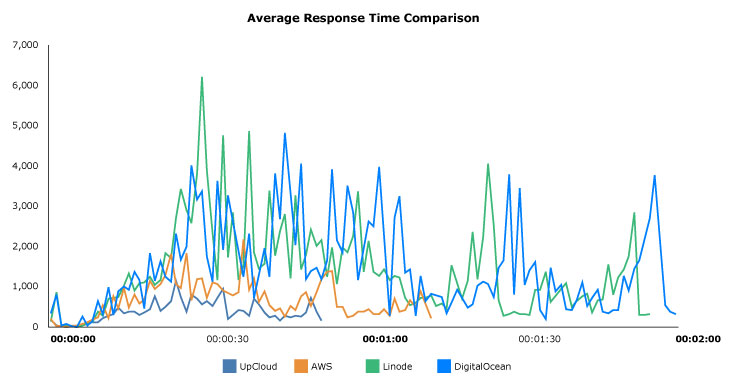
The average response time comparison above shows how higher average latency results with the whole test taking longer to complete. The difference between the highest and lowest points in the path display the response time deviation. It is especially visible on the slower cloud servers running the same Magento configuration.
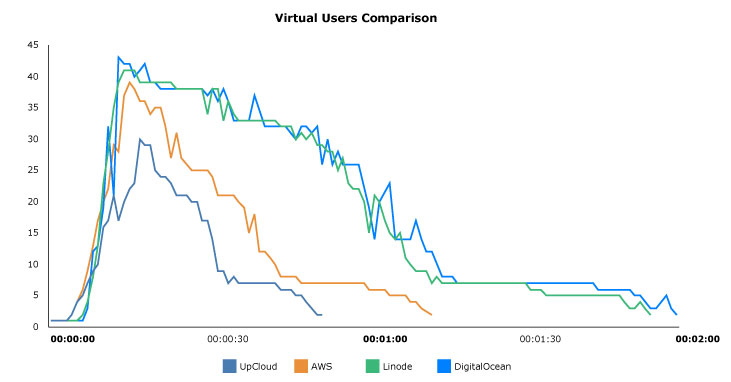
The number of concurrent virtual users in the above graph demonstrates the hosts capacity to serve simultaneous customer requests. The lower the peak in the graph, the faster the server was able to reply resulting in a shorter total run time for the benchmark.
Cost normalized comparison
Comparing the servers purely by their system resources demonstrated some very large price differences. To be able to get the full picture, we installed Magento on another set of hosts but this time specced according to equalize monthly running cost.
Due to the minimum requirements, Magento could not be comfortably set up on the AWS EC2 platform at a comparable cost to the others. Consequently, we opted to include their Lightsail service in the comparison at the $40/month price point instead.
| Normalized by monthly running costs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWS Lightsail | DigitalOcean | Linode | UpCloud | |
| Configuration | 2 CPU / 4 GB / 60GB | 4 CPU / 8 GB / 160 GB | 4 CPU / 8 GB / 96 GB | 4 CPU / 8 GB / 160 GB |
| Throughput | 1225.178 / minute | 1775.772 / minute | 2088.746 / minute | 2787.807 / minute |
| Average | 818 ms | 447 ms | 266 ms | 149 ms |
| Deviation | 1641 ms | 937 ms | 535 ms | 266 ms |
| Latency | 7.5 ms | 12.6 ms | 11.7 ms | 17.6 ms |
| Cost | $ 40 | $ 40 | $ 40 | $ 40 |
In these instances, it is apparent how Magento hugely benefits from the increased CPU power. Both Linode and UpCloud cloud servers saw consistent performance improvements from the additional processor cores.
While the additional system memory from the Linode 8GB plan can be used by the other software running on the same server, it did not appear to largely benefit Magento in our tests.
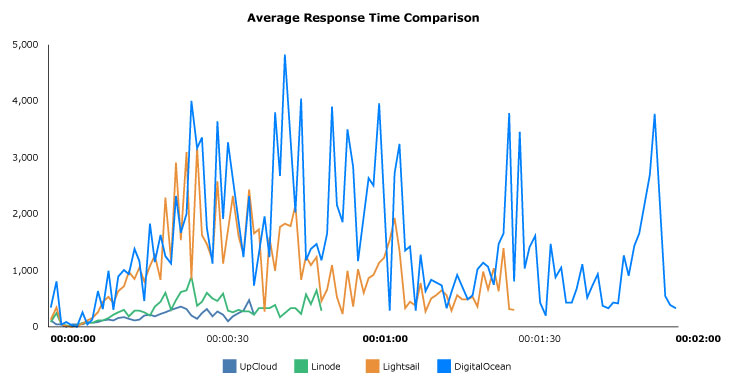
Again in the average response results above, the lower and smother the graph the faster the server was able to respond. Higher peaks and larger deviation in the graph indicate how the slower servers had particular delays in replies to certain requests.
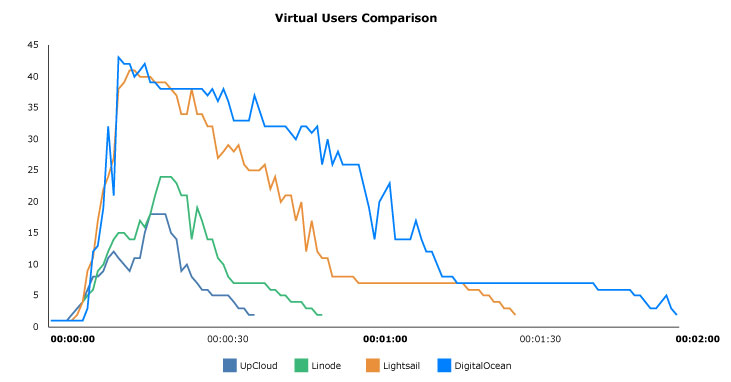
The even shorter benchmark runtimes as compared to the previous results clearly show the benefits of the additional CPU performance. The simultaneous virtual users peaked at far lower numbers for both the Linode and UpCloud cloud servers.
With the higher overall throughput, Magento installed on UpCloud will be capable of serving a far greater customer base than most of our competitors.
Conclusions
In the public cloud environment, your server performance is determined not only by the resources allocated to the instance. Much of the final throughput comes from the underlying hardware and the load generated by other cloud servers on the same host machine. As can be seen from comparing the results of both tests, Magento is very much dependent on the processing capabilities to serve every visiting customer in a timely manner.
With the balanced Simple plans and the benefit of the easily scalable Flexible plan configurations, UpCloud offers the best performance across the board. With the ability to increase server resources at a moments notice, you can have the capacity to close every sale without breaking the bank on running costs.
Want to benchmark the most popular eCommerce platform yourself? We have documented the whole process of installing Magento, configuring the server for load testing, and of course how to run the benchmark.
Check out our use case on eCommerce optimisation
- Read how Magento’s Global Elite Partner Vaimo, one of the world’s most respected experts in digital commerce, benefited from migrating to UpCloud resulting in a faster time to market with the performance that is required with large eCommerce systems.